
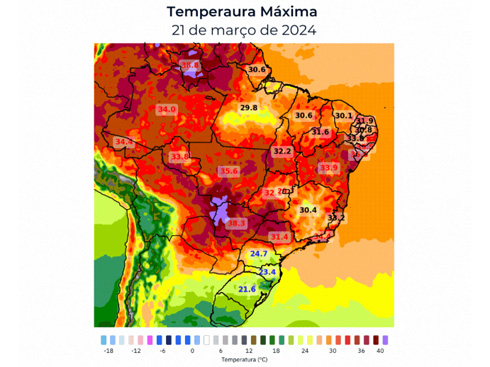
The heat wave that swept through Brazil earlier this month pushed the country's energy consumption to record levels, raising questions about how the heat will affect the growing share of solar power systems. Caetano Mancini, head of marketing and communications solutions strategy at Tempo OK, a Brazilian weather data provider, estimates that, given the heating effect of photovoltaic systems, efficiency losses during the last heatwave could reach 15%. The ideal operating temperature of solar panels is about 25 C. At least that's the case with industry testing and evaluation standards. On average, when the panel temperature exceeds 25 degrees Celsius, the efficiency of the photovoltaic system decreases by 0.4 percent for every degree [Celsius] increase. Despite the loss of efficiency caused by high temperatures, the popularity of solar power in meeting load demand is still increasing, because photovoltaic power generation coincides with the peak demand associated with high temperatures.

The Global Solar Council and the Global Wind Energy Organization are working together to develop standardized basic training for PV technicians, starting with utility-scale solar. The Solar Training Standards Program will set industry-wide standards to ensure the safety, quality and growth of the solar PV workforce. It will begin work on standardized training modules that include learning objectives covering the most common workflows as well as hazards and risks for utility-scale solar technicians. The Global Solar Council says the training will be closely aligned with guidelines and job role definitions already issued by representative bodies such as the American Clean Energy Council's Entry Level Solar Technician Training Guide. Assessments conducted by the Global Solar Council and stakeholders of the Global Wind Energy Organization indicate that the training standards will avoid large-scale duplication across the industry and may reduce transaction costs and increase productivity. The initiative is expected to help asset owners and developers recommend industry-approved safety training for their engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contractors.
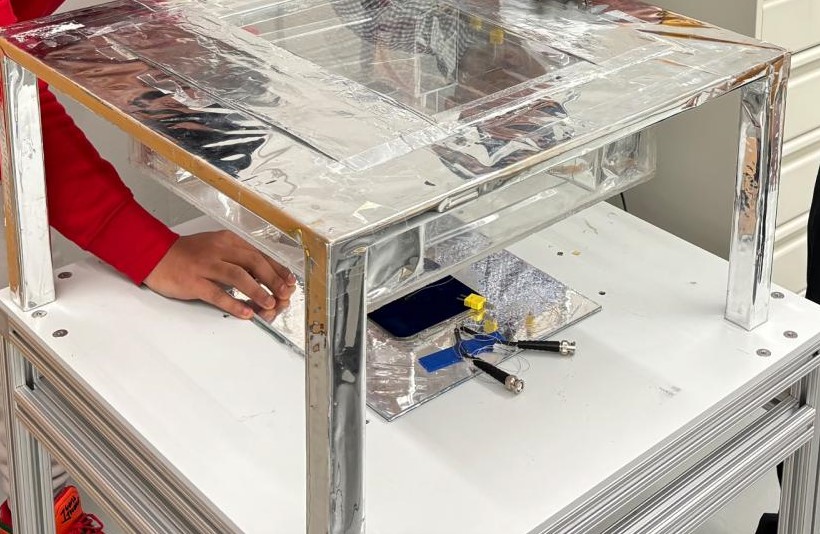

Researchers at Penn State University in the United States have created a hybrid energy system prototype that integrates solar cells for electricity generation and radiative cooling for external cooling. Radiative cooling occurs when an object's surface absorbs less radiation from the atmosphere than it releases. As a result, the surface loses heat and the cooling effect can be achieved without the need for electricity. "The photovoltaic power generated by the dual system can be used either for energy storage or converted to alternating current by an inverter," the scientists said, "the low temperatures obtained on the transparent radiant cooler can be used to cool air or liquid, which can be driven by a fan or pump respectively to interact with the thermal system to save energy." The system consists of a transparent low-iron glass radiant cooler capable of transmitting 91% of sunlight, a transparent infrared opaque layer, and a 125 mm × 125 mm cross-back contact (IBC) photovoltaic cell supplied by US manufacturer Maxeon. There is no direct radiant heat exchange between the radiant cooler and the photovoltaic unit.

The Indian government, through the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), has long supported domestic solar PV cell and module manufacturers, mainly through the Domestic Content Requirement (DCR) policy permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO). The policy aims to boost the growth of the domestic solar industry and reduce dependence on imports. To ensure the integrity of this policy and prevent its misuse, the MNRE issued an Office Memorandum (OM) on February 20, 2018. Under the OM, strict action will be taken against any non-compliance under the MNRE scheme or scheme in the event that a DCR is enforced in a manner consistent with WTO regulations on solar photovoltaic power generation projects. These actions include instituting criminal proceedings under the relevant provisions of the Indian Penal Code, such as IPC 420, which involves fraud. In addition, developers found to be in breach may face blacklisting for up to 10 years, forfeiture of the relevant bank guarantees, disciplinary action against the Central Public Sector Unit (CPSU) or the responsible official of the state government, and any other appropriate measures. However, concerns have resurfaced that the supply of solar PV modules under the MNRE scheme or the scheme may not be fully compliant with the DCR requirements set out in the respective scheme or the scheme. In response, the MNRE reiterated the importance of strict compliance with the DCR provisions under its plan or program. It warned that any violations would result in the same harsh action as outlined in previous memos. The reaffirmation of these guidelines underscores the government's commitment to maintaining the integrity of solar policy and promoting the development of the domestic solar industry. By ensuring compliance with DCR regulations, the government aims to foster a competitive environment that supports local manufacturers while advancing India's renewable energy targets.

Indonesia's Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (MEMR) has issued MEMR Regulation No. 2/2024, which abolishes net metering for rooftop photovoltaic installations. The country first introduced net metering in November 2018, allowing solar project owners to export excess power to the grid operated by state utility PT PLN to reduce their electricity bills. Since the regulation was introduced, several amendments have been made. The latest policy amendment came into effect on January 30 and guarantees that customers who have installed rooftop solar systems before that date will remain under the previous rules for the next 10 years.

The Gestore dei Servizi Energetici (GSE) has released its operating rules for the energy community following the publication of the final rule on January 24. The new rules describe how project developers can receive rebate benefits provided by the Italian government for energy community construction under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNNR), while also explaining how these incentives can be increased at the same time as feed-in tariffs are approved to communities. The new rules also describe how photovoltaic systems deployed before December 15, 2021, will be included in the incentive program. The rules state that these photovoltaic systems can account for up to 30 percent of the energy community's total power generation. The GSE will launch the Developer Incentive Application Platform on April 8.
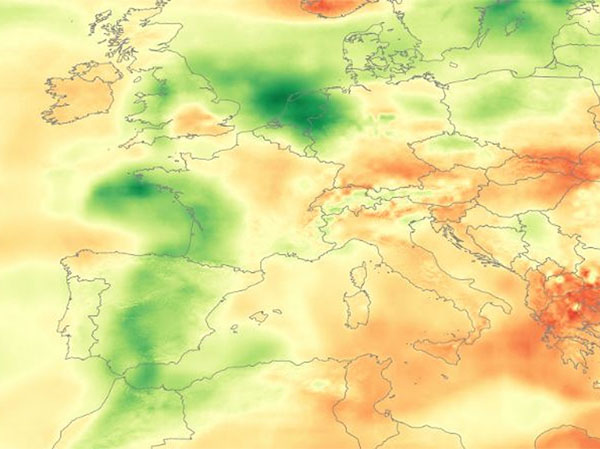
Saharan dust carried by Atlantic winds sweeps across Europe over the Iberian Peninsula. This has led to a decrease in irradiance, particularly in Portugal, Spain, the Netherlands and Germany. Saharan dust carried by Atlantic winds drifted over Europe late last week, reducing daily irradiance by 25 percent as dust in the atmosphere scatters, absorbs and reflects sunlight. Prevailing westerly winds on February 14 carried dust from the Iberian Peninsula to Germany on February 16. Peak irradiance losses were as high as 30% in the affected areas at noon, with large areas of northern Europe, especially the Netherlands, and daily irradiance losses of 15-25% in Germany on 15-16 February. On February 14, a high pressure system over North Africa and a low pressure system in the Norwegian Sea in the low to mid-level atmosphere directed westerly winds across the African continent, carrying Saharan dust from west to east across Europe. Dust in the atmosphere reduces irradiance by scattering sunlight as it passes through the atmosphere, appearing as haze to observers on the ground, and reducing the irradiance received by the surface. Dust can also deposit and contaminate panels, which can affect solar power generation, even after the dust is removed from the atmosphere, reducing the efficiency of power generation. Asset operators in affected areas may find that these pollution impacts result in reduced power generation.

According to the latest monthly report from Camesa, the operator of Argentina's state-owned electricity market, as of the end of December 2023, the cumulative installed capacity of photovoltaic power in the country has reached 1366 megawatts. Camesa also revealed that the country will add approximately 262 megawatts of solar power generation in 2023. The developer added a new photovoltaic power generation capacity of 33 megawatts in 2022, compared to approximately 300 megawatts in 2021. As of the end of December 2023, the installed capacity of photovoltaic systems accounts for approximately 3.1% of the total power generation in the country.

The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, has announced the launch of a residential rooftop solar scheme to provide free electricity. "From substantial subsidies issued directly into the people's bank accounts to substantially concessional bank loans, the central government will ensure that the people do not bear any cost burden," Mr Modi said. "All stakeholders will be integrated into one national online portal." The scheme provides subsidy of INR 30,000 / kW up to 2 kW and subsidy of INR 18,000 / kW for additional capacity up to 3 kW. The total subsidy for systems over 3 kW is capped at INR 78,000.
Categories
New Products
Tin Roof Rapid Solar Mounting System with Hanger Bolt Read More
Residential Small Solar Easy Bracket Kit for Home Balcony Read More
Automatic Single Pile Solar Tracker with 10 PV Panels Read More
Angle Adjustable Aluminum Easy Solar Panel Bracket for Garden Read More
Intelligent Single Post Dual Row Solar Tracking System Read More
5000ES Solar Off-Grid Energy Storage Inverter Supplier Read More
Multi-drive Double Portrait Horizontal Single-axis Tracker System Read More
Double Portrait Horizontal Single-axis Solar Tracker System Read More
© Copyright: 2024 Xiamen Wintop New Energy Tech Co., Ltd.. All Rights Reserved.

IPv6 network supported