Ground solar energy systems use photovoltaic cells (also known as solar cells) to convert sunlight into electrical energy. The following is the working principle of the ground solar energy system:
The working principle of photovoltaic cells: Photovoltaic cells are made of multiple silicon wafers or other semiconductor materials, which have photoelectric effects, that is, they generate current under sunlight. When sunlight shines on the surface of a photovoltaic cell, photons excite electrons, causing them to move in the semiconductor material and generate an electric current.
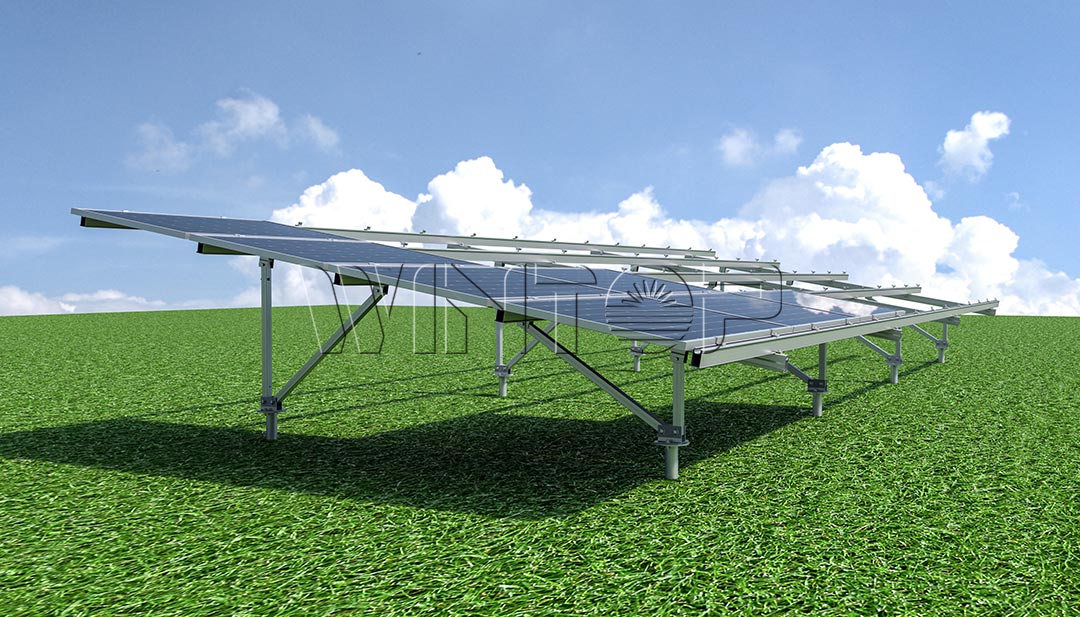 Photovoltaic cells form photovoltaic panels:
Photovoltaic cells form photovoltaic panels: Photovoltaic cells are usually assembled on solar panels, and a large number of photovoltaic panels form a solar array.
Direct current generation: The current generated by photovoltaic cells is direct current, which is converted into alternating current through an inverter and can be connected to the household power system or grid.
Connected to the grid: In a ground solar system, the electrical energy generated by the solar system is connected to the grid through cables. In this way, when the electricity generated by the solar energy system exceeds the demand, the excess electricity can flow into the grid, and vice versa.
Energy storage/transmission: Sometimes, ground-based solar energy systems are equipped with battery energy storage systems to store excess electricity during sunset or cloudy weather for future use. In addition, transmission lines also need to deliver the generated electrical energy to the places where it is needed.
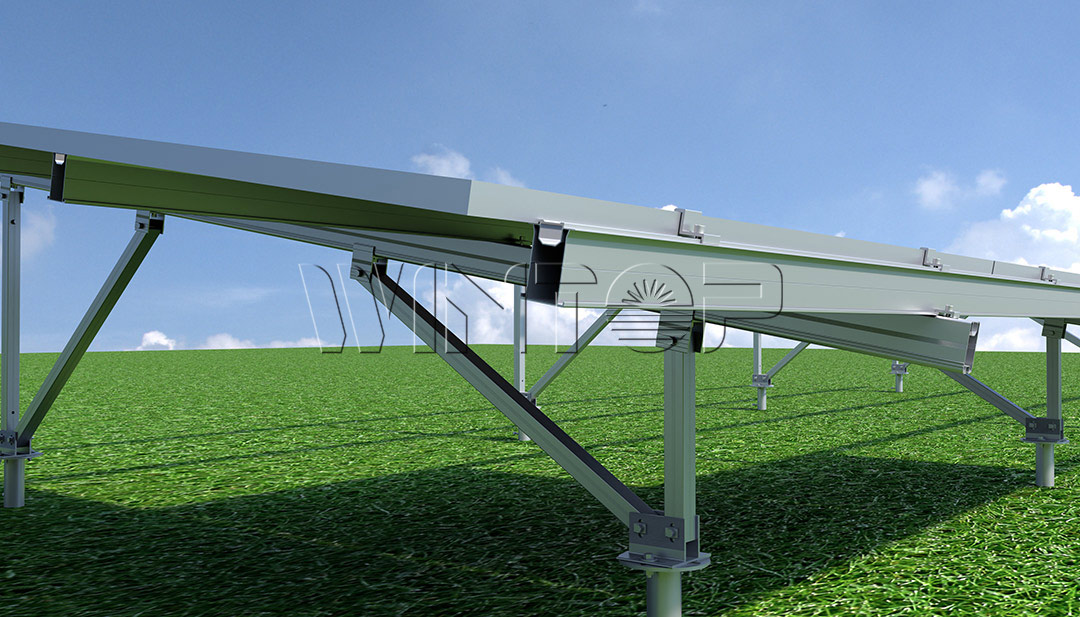

Through the above process, ground-based solar energy systems can convert sunlight into electrical energy and effectively utilize this clean and renewable energy source to power homes, businesses, and even cities.




